Evaluation of Barriers to Knowledge Sharing Affecting Employees’ Innovative Behavior with an Emphasis on Ethics and Social Responsibility Using a Group Best–Worst Method (BWM)
Organizations need creative and innovative employees to improve performance and achieve sustainable competitive advantage. One of the key factors in shaping innovative behavior is knowledge sharing among employees. In this regard, work ethics and social responsibility are two factors that can positively influence the knowledge-sharing process. However, there are various barriers in the path of knowledge sharing, the intensity and nature of which differ across organizations depending on their cultural and structural characteristics. Therefore, identifying and evaluating these barriers is essential for every organization. In this study, in order to identify and prioritize the barriers to knowledge sharing affecting employees’ innovative behavior with an emphasis on ethics and social responsibility, the Best–Worst Method (BWM) was employed as one of the modern and powerful multi-attribute decision-making (MADM) techniques. To this end, by reviewing the related literature and holding expert panel sessions, 24 barriers to knowledge sharing were identified in a thermal power plant, considering the two mentioned factors. Then, using the proposed group BWM algorithm, the identified barriers were evaluated, weighted, and prioritized.The results indicated that strategic, technological, individual, and cultural barriers, respectively, were the most significant obstacles to knowledge sharing in the studied power plant. Moreover 22.93% and 33.68% of the total weight of the identified barriers were related to ethics and social responsibility factors, respectively. The findings highlight the prominent role of these two factors in improving organizational knowledge sharing. Accordingly, organizations seeking business success should focus on ethics and social responsibility to identify, assess, and eliminate the main barriers to knowledge sharing. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm can serve as a reliable, efficient, and valid method for solving MADM problems.
An Overview of the Researches Conducted in the Field of Evaluating the Performance of Pension Funds Using Data Envelopment Analysis
In this research, a description of methods based on data envelopment analysis, including CCR, BCC, SBM, envelopment analysis with combined data (MV-DEA) and a two-stage network method, is described. Also, types of pension funds from different perspectives, including defined benefit (BC) and defined contribution (DC) and mixed, private and public, open and closed, socially responsible (ethical) and irresponsible (immoral) funds, independent funds, semi-independent and complete are introduced. Using the aforementioned analytical methods, the efficiency of each type of fund is compared with other funds and their performance is evaluated (overview). By observing the obtained results, we find that one of the reasons for the diversity in the conclusions can be the difference in the selection of input and output data for each research.
Mathematical Modeling of Data-Driven Multi-Objective Production Planning with Machine Learning in the Biopharmaceutical Industry: Integrating Demand Forecasting and Sustainable Optimization
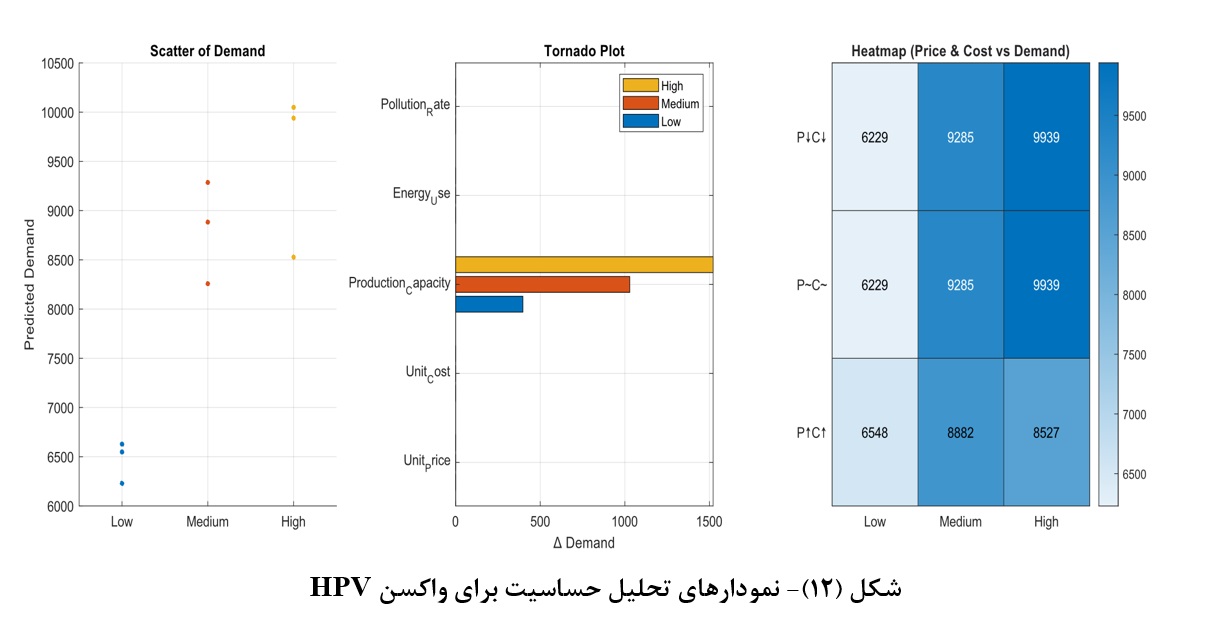
The biopharmaceutical industry, as one of the most advanced sectors of the modern pharmaceutical field, faces multiple challenges such as demand fluctuations, resource constraints, complex manufacturing processes, and environmental requirements. In this context, data-driven and intelligence-based approaches can play a key role in improving decision-making accuracy, sustainability, and profitability. This study aims to develop a comprehensive framework for sustainable production planning by integrating demand forecasting with multi-objective mathematical modeling. In the first step, real data for nine selected drugs were collected over a 36-month period and used to forecast demand patterns through Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. The results showed that the ANN model, with a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 868, was able to reconstruct demand trends with moderate accuracy, while the LSTM model estimated average demand with an error of less than 1% at the drug–scenario level. In the second step, a multi-product and multi-objective mathematical model was designed to simultaneously address economic goals (profit maximization and cost reduction) and environmental goals (pollution and waste minimization). To solve the model, Genetic Algorithms (GA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) were applied in combination with the epsilon-constraint method to extract the Pareto front. The findings revealed that GA had relative superiority in faster convergence, whereas PSO performed better in broad exploration of the solution space. Moreover, multivariate sensitivity analysis indicated that production capacity, raw material cost, and emission rates have the greatest impact on the results. By bridging the gap between demand forecasting and production optimization, this research provides a practical framework for intelligent decision-making in Iran’s biopharmaceutical industry and can contribute to supply chain resilience, cost reduction, and achieving sustainable development goals.
Designing a Self-Assessment System Based on the Sermon of Hammam and Analysing the Interrelations Between Its Various Sections
This article presents and designs a confidential self-assessment system based on the "Sermon of Hammam" (Khutbah al-Hammām), aimed at measuring individuals' alignment with the characteristics of the God-conscious (muttaqin) as described in the sermon. The system utilizes a comprehensive questionnaire composed of statements focused on moral, spiritual, and behavioral traits, allowing users to evaluate themselves based on religious and faith-based criteria. Users rate themselves on statements related to behaviors such as honesty, humility, avoidance of extravagance, and night worship using a scale from 1 (never) to 5 (always). The system’s methodology consists of three main stages, the first one is data collection and assessment. A questionnaire made up of specific statements—such as avoiding excess and speaking kindly—is developed, and participants provide quantitative responses. Each person’s score is calculated by summing the points from the questionnaire items. The second one is results analysis. Each individual’s total score is compared against the maximum possible score (200), and the percentage of alignment with the sermon’s standards is calculated. The results are presented to the user as a natural number between 0 and 100. The lowest-scoring behaviors or traits—those needing improvement—are highlighted and accompanied by related sayings from different resources to encourage reflection and provide guidance. The third one is providing improvement suggestions. If low scores are identified, suggestions for improvement or deeper reflection on the mentioned traits are offered to the user. This process supports the enhancement of users' moral and spiritual excellence. Finally, by collecting responses and calculating the correlation coefficient, the strongest relationship was found between questions related to worship and those related to piety. This project is developed with the aim of encouraging individuals to improve their spiritual traits and offers practical methods for personal development. It can serve as a valuable tool for the community.
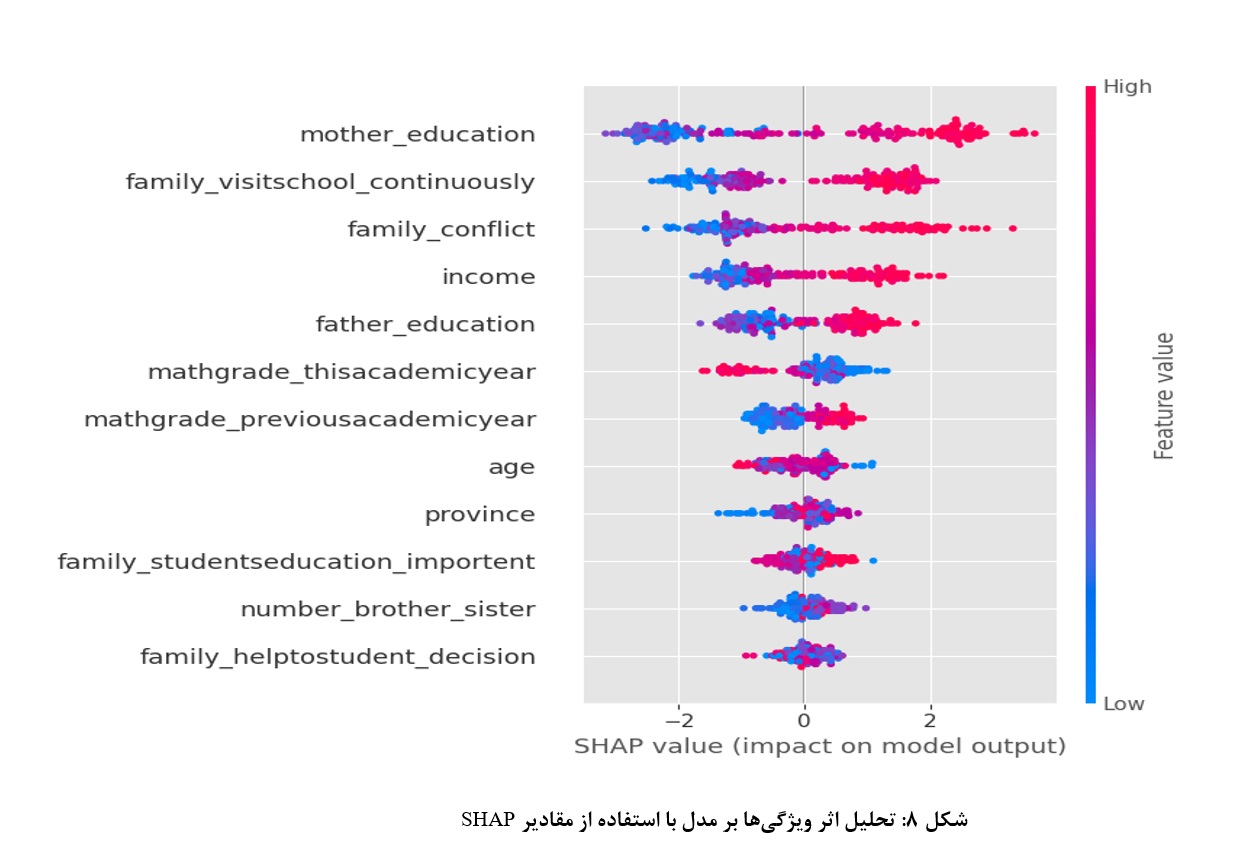
Providing an Intelligent Model for Predicting Student Academic Decline with Emphasis on Family Characteristics: A Case Study of Alborz Province
The education system, as one of the fundamental pillars of human development, plays a crucial role in fostering individual and social advancement. Student academic decline is one of the serious challenges in this field, with long-term individual and social consequences. Although numerous studies have been conducted globally, local research in this area remains limited; therefore, conducting a case study in Alborz Province can help fill this research gap. This study aimed to analyze and model student academic decline based on family indicators through a case study in Alborz Province. The research data were collected from primary and secondary schools in the province and included variables such as parents’ educational level, household income, parents’ occupations, and family structure. To design the predictive model for academic decline, four machine learning algorithms were applied: logistic regression, support vector machine (SVM) with an RBF kernel, random forest, and XGBoost. The results showed that among the tested models, the random forest algorithm performed best and achieved 98% accuracy in identifying complex relationships among the variables. For analyzing the relationships between family variables and academic decline, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was first used to examine statistical associations. Then, SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis was employed to interpret the decisions of the machine learning models and clarify the role of each variable. Based on the findings, mother’s education, household income, and father’s education were identified as the most significant factors contributing to academic decline. The results of this study can be highly effective in designing preventive educational policies and timely identification of at-risk students.
Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT in Human Resource Management: Opportunities, Challenges, and Strategic Insights
The merger of ChatGPT and human resources management (HRMs) is transforming the way firms manage their workforces. This white paper addresses the primary benefits and obstacles of applying the ChatGPT in human resource management, providing a complete analysis of its effectiveness, integrity, and impact on decision-making. ChatGPT enhance HR operations by automating repetitive tasks, decreasing biases in hiring and performance review, and enabling individual employee development programs. It also allows data-driven decision-making through predictive analytics and delivers significant insights into employee performance and engagement. However, successful deployment of a ChatGPT involves seamless interaction with existing systems and constant learning and modification to meet privacy and security concerns. Ethical considerations, such as transparency and justice, are vital to creating confidence and guaranteeing the responsible use of AI. Based on real-world applications and first-time user experiences, this paper gives strategic advice for HR professionals and businesses to employ ChatGPT successfully and build a more efficient, inclusive, and data-driven HR environment.
A Methodological Framework for Designing Business Intelligence Systems Aligned with Strategic Goals and Organizational Processes
Purpose: This study aims to present a systematic method for designing a Business Intelligence (BI) system based on the strategic goals and processes of the organization.
Method: This descriptive study targets managers within the pump and electric motor manufacturing industries as its statistical population. The research was designed and carried out in three stages. In the first stage, the strategic goals of the organization were evaluated in terms of the possibility of participating in business intelligence systems. For this evaluation, four main criteria were used, which were derived from a previous study. Data for this phase were collected through expert-completed evaluation matrices then using the Shannon entropy statistical method, the weights of the criteria were calculated and a score was assigned to each goal. Goals with scores higher than 0.8 were selected for participation in the design of the BI system. In the second stage, a matrix was designed to examine the impact of process groups on the selected goals, and expert opinions were gathered using a five-point Likert scale. Given the uncertainty in the responses, data analysis was conducted using fuzzy logic. After defuzzification, the processes that influenced the strategic goals were identified. In the third stage, key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with the selected processes and goals were identified. This analysis was carried out using the Delphi technique over five rounds to reach a final consensus. The finalized indicators were selected as the core components of the organization's Business Intelligence system.
Findings: The final outcome of the study is an operational framework for designing a Business Intelligence system based on the organization's strategic goals and processes.
Conclusion: By identifying goals that can be supported by business intelligence and applying the proposed methodology, the ability to monitor the achievement of strategic goals is provided, leading to improved organizational productivity.
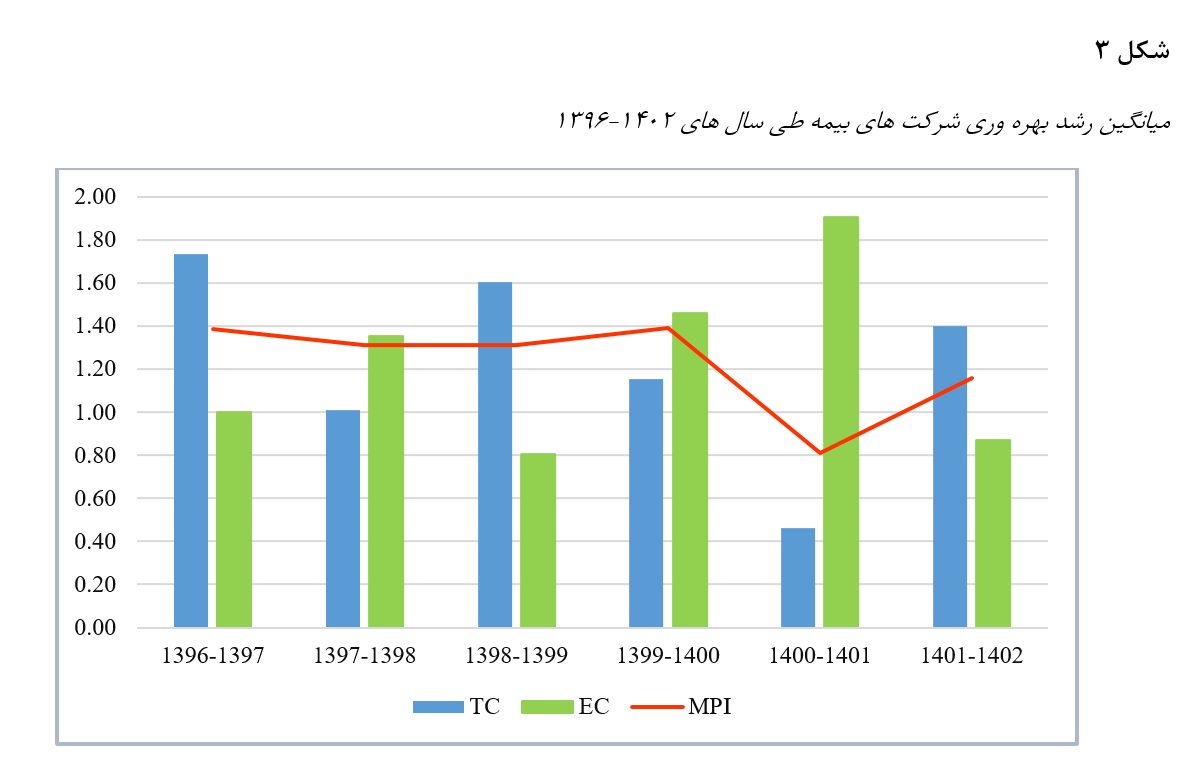
Analysis of Efficiency and Productivity Growth in Iran’s Insurance Industry: A Data Envelopment Analysis Approach
The insurance industry is one of the vital pillars of the financial system, playing an essential role in risk management, enhancing economic resilience, and facilitating investment. It has gained increasing significance in emerging and volatile economies such as Iran. The present study aims to evaluate the performance and analyze the productivity trends of Iranian insurance companies from 2017 to 2023 using the Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) approach. Specifically, the non-radial Russell model and the Malmquist productivity index were applied. Additionally, the impact of contextual variables such as capital, number of branches, and company age on efficiency was examined through a linear regression model. For this purpose, the GAMS software was utilized. The findings indicate that during the studied period, Iran’s insurance industry experienced an unstable and predominantly declining trend in efficiency, particularly in critical years such as 2021–2022, when there was a sharp drop in technological and productivity indicators. However, in some years, there were signs of performance recovery and potential capacity for growth. The results also reveal that increasing capital alone did not guarantee improved efficiency, as traditional or inefficient structures hindered the optimal utilization of resources.
About the Journal
About Us
The Decision Science and Intelligent Systems is a leading scientific journal dedicated to advancing the fields of decision science and intelligence systems by the help of operations research (OR), data envelopment analysis (DEA), and mathematical modeling. We publish original research and review articles that contribute to the theoretical and practical understanding of these disciplines.
Our Mission
Our mission is to provide a platform for researchers and practitioners to disseminate their cutting-edge findings and foster collaboration within the scientific community. We aim to promote innovation, rigor, and the application of scientific methodologies to solve real-world problems.
Scope of Coverage
The journal covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Decision analysis and optimization
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence
- Operations management and logistics
- Data envelopment analysis and performance evaluation
- Mathematical modeling and simulation
- Applications in various domains, such as healthcare, finance, and sustainability
Audience
The journal is targeted at researchers, academics, industry professionals, and policymakers interested in the latest advances and applications of decision science and intelligence systems.
Current Issue